Our solar system includes the Sun, eight planets, five officially named dwarf planets, and hundreds of moons,
and thousands of asteroids and comets. Our solar system is located in the Milky Way, a barred spiral galaxy with
two major arms, and two minor arms. Our Sun is in a small, partial arm of the Milky Way called the Orion Arm, or
Orion Spur, between the Sagittarius and Perseus arms. Our solar system orbits the center of the galaxy at about
515,000 mph (828,000 kph). It takes about 230 million years to complete one orbit around the galactic center.
Orbit Distance(AU) | 
: Average distance from the Sun measured in astronomical units (1 AU ≈ 149.6 million
km, distance from Earth to the Sun).
Equatorial Radius(km) | 
: The distance from the center of the planet to its equator, defining the
planet's
size at its widest point.
Volume(km3) | 
: The total three-dimensional space occupied by the planet.
Mass(M⊕) | 
: The mass of the planet relative to Earth’s mass (1 M⊕ = Earth's mass = 5.9722×10
24kg).
Density(g/cm3) | 
: Average mass per unit volume, indicating the planet's composition (e.g., gas giants
have
lower density than rocky planets).
Surface Gravity(m/s2) | 
: The gravitational pull experienced on the planet's surface.
Escape Velocity(km/h) | 
: The minimum speed needed to break free from the planet’s gravitational pull
without further propulsion.
Rotation Period(Earth Days)

: The time taken by the planet to complete one full rotation on its axis.
Orbit Period(Earth Years) | 
: The time required for the planet to orbit the Sun once.
Mean Orbit Velocity(km/h) | 
: The average speed of the planet as it travels along its orbit around the
Sun.
Orbit Eccentricity | 
: A measure of how elliptical (oval) the orbit is, ranging from 0 (circular) to 1
(parabolic).
Orbit Inclination | 
: The tilt of the planet's orbit relative to the plane of the Solar System, measured
in
degrees.
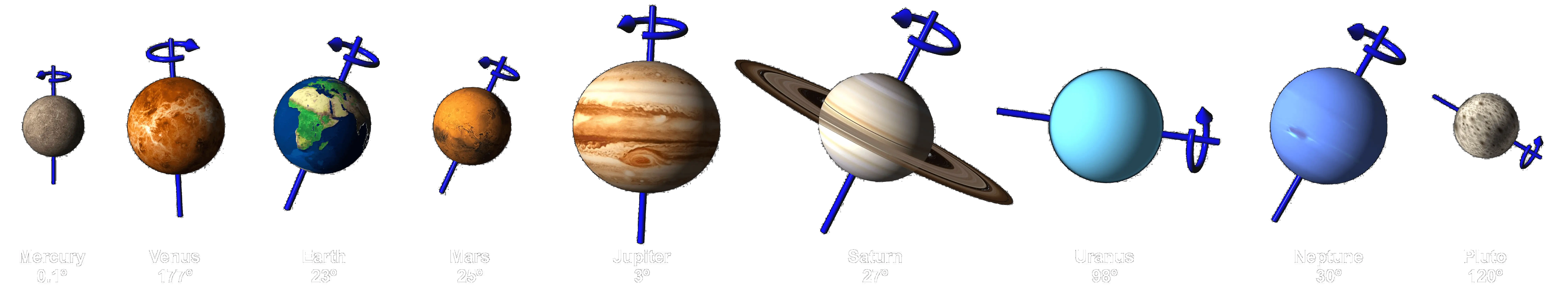
Equatorial Inclination | 
: The tilt of the planet’s equator relative to its orbital plane.
Surface Temperature | 
: Average temperature of the planet’s surface, often varying between the day and
night
sides.
Atmospheric Constituents | 
: Primary gases that make up the planet’s atmosphere.
Moons | 
: The number of natural Moons orbiting the planet.
Rings | 
: Presence of planetary rings.
Axial tilt, the angle between the planet's rotational axis and its orbital axis.
A real-time visualization of our solar system using planetary science data. NASA/JPL-Caltech
NASA/JPL-Caltech
Eyes on the Solar System - James Webb Space Telescope -  NASA/JPL-Caltech
NASA/JPL-Caltech

NASA/JPL-Caltech
NASA/JPL-Caltech